The heart is a tireless worker |
|
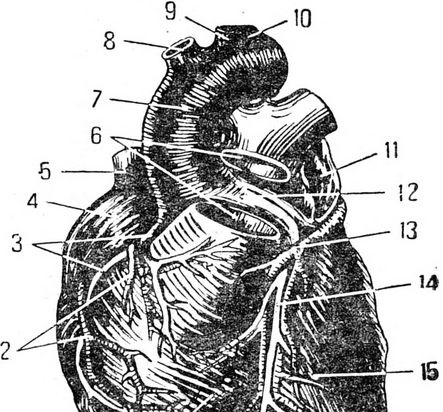
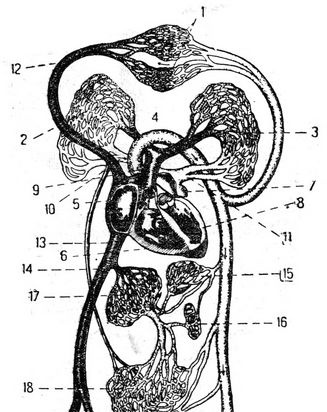
Starting with the weather, which this year did not indulge us, we soon switched to our favorite skate. My new acquaintance threw the phrase that, they say, a heart attack is now fashionable, but that he, thank God, does not threaten him. I must confess that I was very distorted then by the frivolous tone of my interlocutor. Well, if we consider fashion from the point of view of statistics, then a heart attack, of course, is in “fashion”, since most often doctors have to diagnose atherosclerosis. And this disease is to blame for a heart attack. And although a heart attack is not inevitable, but only a probable further course of the disease, it poses a serious threat to human life. So, jokes with him are bad. Noticing the noticeably altered blood vessels on the hands of a fifty-year-old brisk man sitting opposite me, I told him: “If I were you, I would not have renounced a heart attack, because you atherosclerosis». Reading genuine fear in his eyes, I hastened to calm him down. “Everything is still fixable. Much depends on you. But for this you must know well what causes a heart attack and how to prevent its onset ". "A tree is mightier by its roots, and a man is a heart", Says folk wisdom. A strong, healthy heart is the key to good health. Having begun to beat in the womb, it faithfully carries out its service throughout a person's life. The heart and blood vessels form the cardiovascular system, through which blood is delivered to all organs and tissues of our body. The heart is the central organ of the circulatory system; thanks to its rhythmic contractions, blood circulation occurs. So the comparison of the heart with the motor is quite legitimate. What is the structure of this tireless worker? The heart is located on the left side of the chest. Outside, it is protected by the ribs and sternum. In addition, it is also protected by clothing made of dense connective tissue — the pericardium. The heart muscle itself, penetrated by numerous nerves and vessels, is called the myocardium. The inner part of the myocardium - the endocardium - is a smooth elastic membrane. The heart consists of four cavities: two atria and two ventricles. Between each atrium and the corresponding ventricle there is an opening closed by a sail-shaped or cuspid valve, which is formed by the folds of the inner shell. Heart (front view): 1 - right ventricle; 2 - anterior veins of the heart; 3 - the right coronary artery; 4 - right ear; 5 - superior vena cava; 6 - pulmonary artery; 7 - aorta; 8 - unnamed artery; 9 - left common carotid artery; 10 - left subclavian artery; 11 - left ear; 12 - left coronary artery; 13 - a large vein of the heart; 14 - anterior descending branch of the left coronary artery; 15 - left ventricle; 16 - apex of the heart. The valves open to the inside of the ventricles, and thus blood can only flow in one direction; from the atrium to the ventricle. Large vessels depart directly from the ventricles: from the left - the aorta, from the right - the pulmonary artery. Gradually branching, the aorta ends in tiny capillaries. Through them, nutrients and oxygen enter the tissues from the blood, and waste substances and carbon dioxide from the tissues are absorbed and carried away by the blood. How great is the network of capillaries that penetrate into all tissues and organs of the body is shown by a comparison that is used quite often, but which does not become less clear from this. If all the capillaries were stretched in one line, then it could gird the globe along the equator two and a half times.The capillaries, in turn, flow into the gradually enlarging vessels - veins, which deliver to the heart, to its right atrium, blood already containing metabolic products and carbon dioxide. The path of blood flow from the left ventricle to the right atrium is called the systemic circulation. The further path of venous blood goes through the right half of the heart into the lungs - a small circle of blood circulation. On this path, there is an exchange of blood gases: the release of carbon dioxide and its enrichment with oxygen with the help of the lungs. All blood, passing through the lungs in less than one minute, captures about a liter of oxygen, giving the lungs the same amount of carbon dioxide. Imagine now what a huge amount of oxygen the human body consumes during the day! A person can live without food for ten days, and without oxygen he cannot live even ten minutes. From the lungs, oxygen-rich blood enters the left atrium. Again the contraction of the heart muscle - and again the blood begins to run. At the site of the exit of the aorta and pulmonary artery from the ventricles, there are valves, which are called semilunar valves. They open towards the vessels. Their purpose is to prevent the return flow of blood from the aorta and pulmonary artery to the heart. The movement of blood occurs due to contractions of the heart muscle. Themselves, these contractions, although they occur automatically, are due to the influence of nervous stimuli emanating from both the central nervous system and from special nerve nodes embedded in the heart itself. Circulation scheme: 1 - area of capillaries of the upper half of the body; 2 - the area of the capillaries of the right lung; 3 - the area of the capillaries of the left lung; 4 - aortic arch; 5 - right, atrium; 6 - right ventricle; 7 - left atrium; 8 - left ventricle; 9 - pulmonary artery; 10 - right pulmonary veche; 11 - left pulmonary vein; 12 - superior vena cava; 13 - inferior vena cava; 14 - hepatic vein; 15 - the area of the capillaries of the stomach; 16 - area of spleen capillaries; 17 - area of liver capillaries; 18 - the area of intestinal capillaries; 19 - area of the capillaries of the lower half of the body. The following question may arise: why does the heart beat rhythmically, and not drive the blood out in a continuous flow? Many, of course, know that any work is most successful when it is rhythmic and at the right intervals is replaced by rest. So. the heart also works. If it drove blood in a continuous stream, it would quickly get tired. And when it contracts rhythmically, it alternates between work and rest: the contraction lasts 0.3 seconds, and rest for 0.5 seconds. With inflammation of the heart muscle, with excessive expansion of the cavities of the left and right ventricles, as well as with changes, wrinkling of the heart valves, normal blood circulation is upset. A heart defect occurs, in which blood flows not only from the atrium to the ventricle and from the ventricle to the vessels, but also from the ventricle to the atrium or from the vessels to the ventricle. When the muscle contracts and the valves slam open, a sound is produced that is called a heart tone. If the muscle contracts poorly, the tone becomes less sonorous - deaf, and if the valves are broken and they do not completely close the opening or there is a narrowing of the latter, then the blood passes with a noise. The doctor can judge the nature of changes in the work of the heart by the changed heart sounds or the appearance of a noise. Who truly has a fine ear! An experienced doctor not only by tone, but also by the frequency of contractions, pulse, can accurately recognize many ailments. I remember such a legend. The famous physician Sun Si-lu was invited to the wife of the Chinese emperor Tai Zong, who suddenly fell ill. But what was the doctor to do if no one except the spouse had the right to even contemplate her? And there was no question of touching her! But Sun Si-lu was found. He asked the empress, who was “behind the screen, to tie a thin thread to her wrist, and give the other end to him.The Empress decided to play a trick on the doctor, she tied a thread to the paw of a lap dog. The doctor immediately remarked sadly: “You are testing me in vain. The pulse I feel is the pulse of an animal! " The ashamed woman had no choice but to exactly fulfill Sun's request. Leaving, the doctor said to the emperor: “Your spouse is not sick, she is pregnant. Wait for your son "... This prediction came true ... In this legend, of course, as in any other, there is an exaggeration. And the truth is that an unmistakable instinct helps the doctor sometimes even by one pulse to determine the disease. The state of the pericardium also affects the work of the heart. When this heart shirt loosely fits the heart muscle, it does not prevent it from contracting and expanding. If it becomes inflamed and becomes less mobile, then the movements of the heart will be connected, and therefore, blood circulation will be impaired. The work of the heart is determined by the amount of blood flowing in and the amount of resistance that it must overcome. With each contraction, overcoming arterial pressure, the heart ejects a strictly specified amount of blood, giving it the required speed. The intensity of the activity of the heart changes most of all depending on the conditions in which the body is located, in particular on the degree of muscle activity. With complete physical rest, especially during sleep, the heart works less, the heart rate is, for example, in an adult 60-75 per minute, and the amount of blood thrown out is about 4-5 liters. With muscle activity, the heart has to contract more often. With the maximum muscular load for a given individual, the frequency of heart contractions increases many times. But only a healthy, well-trained heart has such a great reserve power. The explanation is simple: the greater the load on the muscles, the more they need food and oxygen. Hence, the heart also needs to work hard. Physiologists have been able to calculate that even a relatively small amount of stress, such as climbing stairs, requires five times more effort than, for example, walking on level ground. The heart muscle, like any organ, also needs oxygen and nutrients to perform its duties, that is, the supply of arterial blood. The heart is nourished by the right and left arteries extending from the very mouth of the thoracic aorta. They cover the heart with a crown, therefore they are called coronal or coronary. The branches of these coronary arteries run throughout the heart. The left coronary artery supplies blood to most of the left side of the heart, the anterior part of the interventricular septum, and the anterior part of the right ventricle. It is more powerful than the right one, and passes through itself about three quarters of the amount of blood that the heart needs. The right coronary artery fell to feed most of the right half of the heart, the posterior part of the interventricular septum, and part of the posterior wall of the left ventricle. The tortuosity of the coronary arteries promotes better filling of the coronary vessels with blood under the infinitely changing conditions of the heart. Up to 10% of the blood flows through the coronary vessels and is thrown out per minute into the systemic circulation. Therefore, the heart muscle is equipped with a capillary network that is twice as abundant as the skeletal muscle. The better the heart muscle feeds on blood, the greater its ability to develop energy, the less it needs to stretch in order to induce the corresponding contraction force, and the more normally its functions are performed. With insufficient blood flow and poor oxygen enrichment, oxygen starvation of the heart muscle can occur, which causes pain in the heart. Shapiro Ya.E. - They don't joke with the heart Similar publications |
| Normal sleep | A little about the culture of lifestyle |
|---|
New recipes
 Once I stopped by my close friend to while away an hour or two together. He had a guest, already an elderly man, apparently quite healthy.
Once I stopped by my close friend to while away an hour or two together. He had a guest, already an elderly man, apparently quite healthy.